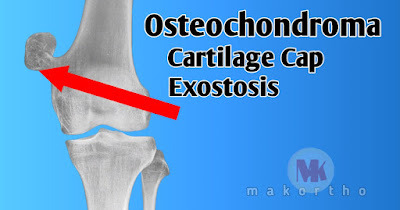
Definition-
Small over growth at the edge of physeal plate with endochondral ossification
develops into a bony protuberance covered by cartilage cap.
Type-
Solitary, Multiple (HME),
Sessile(broad base), Pedunculated (Narrow base)
Clinical Feature:
One of the commonest benign bone tumour,
Common site--any bone may involved, fast growing end of long bone, Iliac Crest
Age-Teenager, young adult (any growth after growth period-indicates-suggestive
of malignant transformation.
•Lump,
•Pain
•Paresthesia (rare)
•Multiple exostosis--when develop as a part of hereditary disorder.
X-ray-
Appearence is pathognomic,-
Well defined exostosis at metaphyses,
Looks smaller than feels,
Large lesion shows exostosis surrounded by clouds of calcified materials.
Pathogenesis:
The pathogenesis of osteochondroma involves a genetic mutation leading to
abnormal bone and cartilage growth.
There is abnormal endochondral ossification in the region where the
osteochondroma forms.
Under the influence of abnormal signaling Chondrocytes may fail to interact
properly with the surrounding periosteum,
Abnormal proliferation of cells in the metaphyseal region.
Gene mutation in one of two gene -EXT1 Or EXT2. EXT1 located in chromosome
8q24.11-q24.13,And EXT2 located in chromosome 11p11-12.
Pathology-
At operation-cartilage cap is seen surmounting a narrow base or pedicle, cap is
hyaline cartilage,
Large lesion-Cowliflower appearence,degeneration and calcification in centre of
cartilage
The cartilage cap contains chondrocytes. With variations in size and shape, in a
columnar cell fashion and Lack of Cellular Atypia.
Cancellous Bone Core
Periosteal Reaction (optional)
Treatment:
Symptomatic- Excision,
Rapid enlarging-Urgent operation,
If any suspicion- Imaging and Staging and Biopsy,
If features like a benign lesion but certain to be enlarging- treat as
chondrosarcoma.
Complication:
Chance of malignancy -
1% in solitary lesion,
6% in multiple lesion.
Signs of malignant transformation-
Rapid and progressive enlargement,
Bulky cartilage cap,
Scattered flecks of calcification in cartilage cap,
Soft tissue spreading.





0 Comments