BONE TUMOUR
•Definition:
•Defined
as abnormal growth of cells in bone tissue and its components.
Diagnosis :
•Clinical
Feature
•Investigation
•Clinical Feature—
•History-Present
, Previous, Life style
•Age- •Childhood and adolescence- Benign
tumour,
Ewing’s sarcoma, Osteosarcoma.
•Old age- Chondrosarcoma,
•Pain
-
•Swelling-
•Neurological
symptom
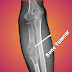
•Pathological
fracture
•Investigation:
•Imaging-
•Laboratory
Findings-
•Histopathology-
•Imaging-
•X-ray
•USG
•CT
•MRI
•Bone
Scan(Radio nuclide Scanning)
•Laboratory Investigation
CBC
ESR Hb%
PTH-------- Brown Tumour
S. Protein electrophoresis
Bence
jone’s
protein
Acid Phosphatase--- Prostatic
Cancer
Alkaline Phosphatase—Non specific
CRP--
•Histopathology- Biopsy
•Closed
Biopsy-
•FNAC, Trephine
Needle
•Open
Biopsy-
•Incisional
•Excisional
Typing, Grading, and Staging.
•Differential Diagnosis
•Soft
Tissue Haematoma
•Myositis
ossificans
•Stress
Fracture
•Tendon
Avulsion
•Bone
Infection
•Gout
•Other
Bone Lesions—
•Fibrous
cortical defects,
•Medullary
Infract
•Bone
Islands
•Principle
Of Management
•Multidisciplinary
team approach
•Best
conducted in tertiary centre
•Consultation
and cooperation between the
• Orthopaedic
surgeon
•Radiologist
•Pathologist
•Oncologist
•Also
be involved- physiotherapist,
Occupational therapist, Prosthetist.
•Methods of treatment—
•Benign
and asymptomatic-
•Small,
and can afford to temporize
•Observation
•Biopsy
is advisable with excision or curettage.
•Benign,Symptomatic,Enlarging-
•Biopsy
for confirm diagnosis,
•Marginal
excision or curettage.
•Suspected Malignant Tumour
•Tumour
Excision-
•Limb
Salvage-Operation (G-II)
•Amputation
•Multi
agent Chemotherapy
•Radiotherapy
•Multi
Agent chemotherapy
•Reduce
the size,
•Prevent
Metastasis seeding
•Improves
survival rates-(combined with surgery)
•Methotraxate
•Doxorubicin
•Cyclophosphamide
•Vincristin
•Cis
platinum.
•Radiotherapy—
•Adjuvent
therapy before operation
•Combined
with adjuvant chemotherapy
•Tumour in
inaccessible site,
•Inoperable
lesion
•Palliative
local control
•Postoperatively-Marginal
or intralesional
excision
•Chance
of post irradiation spindle cell sarcoma, Pathological fracture.



.png)
.png)


.png)

0 Comments